8 Certificate management
8.1.1 Overview
OPC UA applications typically have Application Instance Certificates to provide application level security. They are used for establishing a secure connection using Asymmetric Cryptography. These Application Instance Certificates are Digital Certificates which are X.509 Certificates and contain a list of data items that are defined in Part 4 and completely described in Part 6. These data items describe the Application Instance that the Digital Certificate is assigned to.
The Digital Certificates include a Digital Signature by the generator of the Certificate. This Digital Signature can be self-signed (The signature is generated by the Private Key associated with X.509 Certificate that is the Application Instance Certificate) or can be signed by a Certificate Authority (The signature is generated by the Private Key associated the X.509 Certificate of the CA). Both types of Certificates provide the same level of security and can be used in Asymmetric Cryptography. The Signatures can be generated using a variety of algorithms, where the algorithms provide different levels of security (128 bit, 256 bit, 512 bit ...). The algorithm that is required for signing a certificate is specified as part of the Security Policy. Servers and Clients should be able to support more than one certificate since more than one certificate may be required depending on the Security Profiles that are being supported.
Asymmetric Cryptography makes use of two keys – a Private Key and a Public Key. An application will have a list of trusted Public Keys that represent the applications it trusts. This list of trusted Public Keys is stored either in the Windows Registry or a file folder. It will also have a Private Key that corresponds to its Application Instance Certificate. The application can use a Public Key, from its list, to validate that the signature on a received connection request was generated by the corresponding Private Key. An application can also use the Public Key of the target application to encrypt data, which can only be decrypted using the Private Key of the target application.
8.1.2 Self signed certificate management
The major difference between CA signed and self-signed Digital Certificate is the effort required to deploy and maintain the Digital Certificates. The choice of when to use a CA issued Digital Certificate versus a self-signed Digital Certificate depends on the installation and site requirements.
Figure 7 illustrates the work that is required to maintain the trust list for self-signed Digital Certificates.
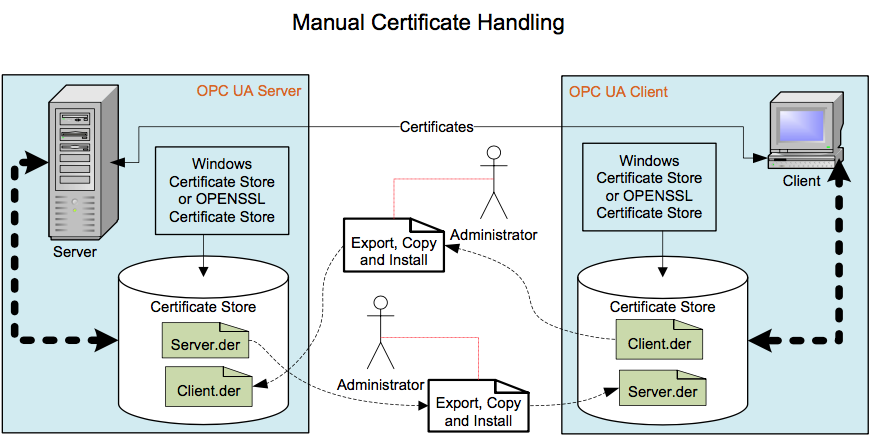
An administrator would be required to copy the Public Key associated with all Client applications to all Server applications that they may need to communicate with. In addition, the administrator would be required to copy the Public Key associated with all Server applications to all Client applications that may need to communicate with them. As the number of Servers and Clients grows, the administration effort can become too burdensome. In addition, a Digital Certificate has a lifetime and will need to be replaced with an updated Digital Certificate at some point in time. This will require that new Private Keys and Public Keys be generated and all of the Public Keys to be copied again. In very small installations, explicitly listing what Clients a Server trusts by installing the Public Key of the Client Application Instance Certificate in the Trusted Certificate store of the Server may be acceptable.
8.1.3 CA Signed Certificate management
In systems with multiple Servers and Clients the installation of Public Keys in Trust Lists can very quickly become cumbersome. In these instances, the use of a company specific CA can greatly simplify the installation/configuration issues. The CA can also provide additional benefits such as management of Digital Certificate expiration and Certificate Revocation Lists (CRL). Figure 8 provides an illustration of this activity.
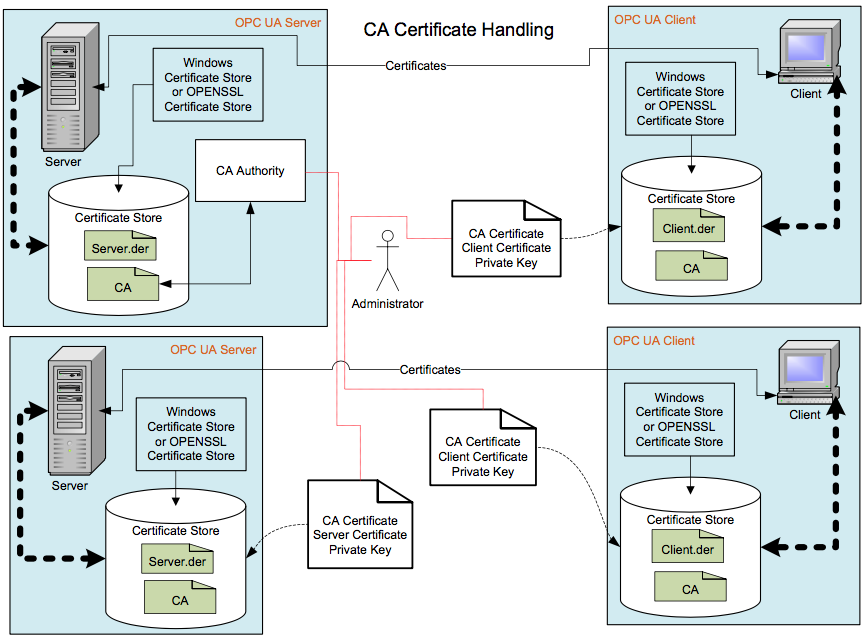
The administrator will need to generate a CA signed Application Instance Certificate for all Clients and Servers that are installed in a system, but he will only need to install the CA Public Key on all machines. When a Digital Certificate expires and is replaced, the administrator will only need to replace the expired Digital Certificate (Public Keys and Private Keys), there will be no need to copy a Public Key to any locations. The company specific CA allows the company to control the issuing of Digital Certificates. The use of a commercial CA (such as VeriSign) would not be recommended in most cases. An OPC UA Application typically is configured to trust only the other applications determined by the Company as trusted. If all Digital Certificates issued by a commercial CA were to be trusted then the commercial CA would be controlling which applications are to be trusted, not the company. Certificate management needs to be addressed by all application developers. Some applications may make use of Certificate management that is provided as part of a system wide infrastructure, others will generate self-signed Digital Certificates as part of an installation. See Part 12 for additional details on system wide infrastructures for Certificate management.
8.1.4 GDS Certificate Management
8.1.4.1 Overview
In some systems, a GlobalDiscoveryServer with Certificate Management may be deployed. The GlobalDiscoverServer will either push certificates to Clients and Servers or allow Servers and Clients to pull certificates. The GlobalDiscoveryServer certificate management can manage all certificate deployments; this includes TrustLists, CAs and CRLs. 8.1.4.2 Developers Certificate management From a developer point of view, it is a best practice, if your application supports Certificates, that it automatically provides a self-signed Application Instance Certificate on installation. In addition, the application is able to easily replace the self-signed Application Instance Certificate with a CA issued Application Instance Certificate or have the self-signed certificate signed by a CA. The configuration of a Trust List should also be easily accomplished. Typically, Trust Lists for Public Keys of Application Instances are kept in a separate list than those of a CA. Also an application should be able to handle Certificate Revocation Lists (CRL). These are lists of Public Keys that are associated with a given CA that have been revoked. This allows a CA to remove a Digital Certificate that it had signed from circulation. CRLs are provided by a CA and usually distributed in some automatic manner; see Part 12 for additional details. From a security point of view, it is essential that the Certificate stores used to store Private Keys are protected and secured only allowing read/write access by an appropriate administrator and /or by the application. Trust lists, CRLs, and trusted CA lists are secured allowing only write access by an appropriate administrator and in the case of pull configuration by the application. Read access may be granted to other valid users, but the list of users allowed read access would be a site decision. From an Installation point of view, it is a best practice that a standard tool to generate an Application Instance Certificate is provided. This tool could be one provided by an OPC UA SDK vendor or by the OPC Foundation. The standard tool ensures that the Application Instance Certificates that are generated include all of the required fields and settings. A particular OPC UA application shall be able to accept and install any valid Application Instance Certificates generated by external tools. The choice of the actual tool is site specific. Figure 9 provides an overview of some of the key points of Certificate handling.
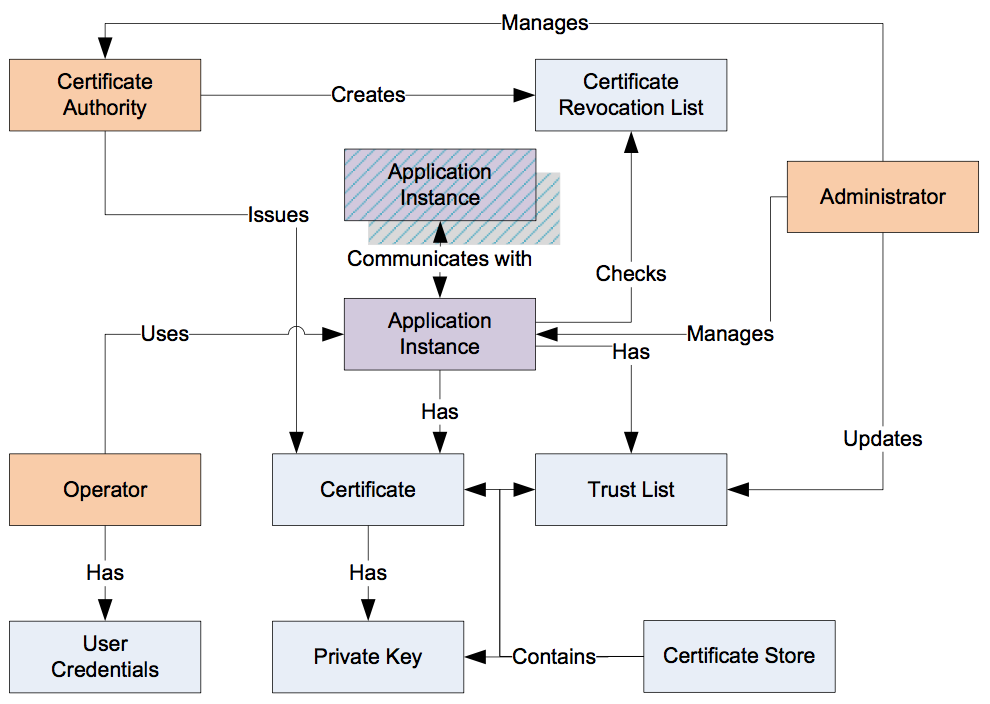
The following is a summary of these key points when a CA based, security required system is deployed:
Application Instance – An OPC UA Application installed on a single machine is called an Application Instance. Each instance has its own Application Instance Certificate which it uses to identify itself when connecting to other applications (the Public Key and Private Key). Each Application Instance has a globally unique URI which identifies it. The application will also check trust lists and CRL’s to determine if access should be granted. The application will communicate using a secure channel established using Asymmetric Cryptography with other applications.
Administrator – The person or persons that administer the Certificate handling associated with a UA system and manage the security settings for Application Instances. This includes setting the contents of trust lists and managing any activities performed by a CA.
Operator – An Operator is person who uses the Application Instance. More than one Operator may exist for any given application. An Operator may have User Credentials which are used to determine access rights and to track activities within the Application Instance. User Credential – A User Credential is a generic term for an electronic ID which identifies an Operator/User. It may be passed to a Server after the Application Instance Certificate is used to create a secure channel. It can be used to determine access rights and to track activities (auditing).
Certificate Authority (CA) – A Certificate Authority (CA) is an administrator or organization which is responsible for creating and managing Certificates (it is usually a partially automated software product). The Certificate Authority verifies that information placed in the Application Instance Certificate is correct and add a Digital Signature to the Certificate that is used to verify that the information has not been changed. Each CA has its own Digital Certificate which is used to create the Digital Signatures. A CA is also responsible for maintaining CRLs. In most cases it is a software package that an administrator periodically reviews or accesses, usually when the software package generates an alarm or notification that some review action is required.
Certificate – A Certificate is an electronic ID that can be held by an application. The ID includes information that identifies the holder, the issuer, and a unique key that is used to create and verify Digital Signatures. The syntax of these Certificates conforms to the X509 specification, as a result, these Certificates are also called “X509 Certificates”. Certificates also have a Private Key associated with them.
Self-Signed Certificate – A self-signed Certificate is a Digital Certificate which has no Certificate Authority. These Certificates can be created by anyone and can be used in situations where the administrators of UA Applications are able to verify the claims by reviewing the contents themselves. A system that uses only self-signed Certificates would not have CA or CRL.
Private Key – A Private Key is a secret number known only to the holder of a Digital Certificate. This secret allows the holder to create Digital Signatures and decrypt data. If this secret is revealed to unauthorized parties then the associated Digital Certificate can no longer be trusted or used. It is replaced or in the case of a CA generated Certificate it is revoked.
Trust List – A Trust List is a list of Certificates which are trusted by an Application Instance. When security is enabled, UA Applications reject connections from peers whose Certificates are not in the trusted list or if the Certificate is issued by a CA that is not in the Trust List.
Certificate Store – A Certificate Store is a place where Certificates and Private Keys can be stored on a file system. All Windows systems provide a registry based store called the Windows Certificate Store. All UA systems can also support a directory containing the Certificates stored in a file which is also called an OpenSSL Certificate Store.
Revocation List – A Revocation List is a list of Certificates which have been revoked by a CA and are not be accepted by an Application Instance.